Oral surgery
![]()
Oral surgery
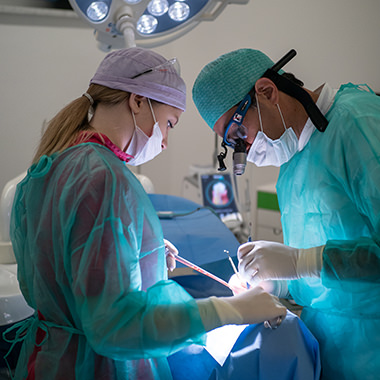
The oral surgery we perform involves procedures that a general dentist cannot perform due to their complexity. The patient may be referred to us by their general dentist.
In the field of oral surgery we perform:Tooth removal
- Removal of wisdom teeth
- Apicoectomy
- Surgical extension of the clinical crown of the tooth
- Fenestration
- Frenulotomy
Services are provided at the expense of the OZZ or the patient is self-funding (prices can be found in the price list).
The course of healing and the possibility of complications
Even with the most diligent work, the complications cannot always be avoided. Minor trauma to the mucosa or bone heals without consequences, bleeding can be stopped by cold compresses and stronger pressure on the wound with a gauze or tampon. Please inform us about the use of medications that cause blood clotting disorders prior to the surgery, as it is required to change the treatment process accordingly.
Highly unlikely but not impossible is nerve damage in the lower jaw, which causes a temporary, rarely permanent decrease in sensation in the lower lip.
In the upper jaw, a transitional opening of the maxillary sinus cavity to oral cavity after tooth extraction may occur due to the root anatomy. In that case, it is important to follow our instructions after the procedure. The healing is mostly spontaneous; if not, additional surgical treatment is required.
Inflammation after tooth extraction
Inflammatory complications after tooth extraction are relatively common and can occur after the removal of any tooth; the likelihood of such complications is greater when the lower teeth are removed. In most cases superficial inflammation of the bone, i.e. alveolar osteitis occurs; other complications are rare. Symptoms appear within 3-4 days after the tooth extraction:
- severe pain that spreads to the ear, eye or neck
- bad breath
- unpleasant taste
Superficial inflammation of the bone occurs due to the breakdown of a blood clot, which fills the extraction wound after the extraction. Why this happens is not completely clear; however, the risk factors that increase the likelihood of this condition are well known:
- smoking
- oral contraception
- failure to follow instructions after tooth extraction
- superficial inflammation of the bone upon previous removal of the tooth
- gum inflammation
No effective treatment is known; pain is relieved with painkillers, and the condition usually subsides within two weeks.
How to avoid complications after tooth extraction?
Complications after tooth extraction can be effectively avoided with placement of fibrin (L-PRF) plugs. A small amount of blood is collected from the upper limb and prepared in a special centrifuge before the procedure. Fibrin plugs are formed from the patient’s blood, inserted into the extraction wound and sutured. The plugs are rich in fibrin, leukocytes, platelets and growth factors that are released from the plug in the days after extraction and make healing faster and more efficient. The possibility of post-extraction complications is insignificant, tissue regeneration is better and faster. The volume of bone that regenerates with the use of a fibrin plug is significantly larger than without its use. Bone deficiency is in many cases a limiting factor in implant therapy that follows.
RECOMMENDATION: If you want to avoid extraction complications with L-PRF plugs, or if you intend to replace the extracted tooth with a dental implant, please let us know before the procedure.
Make an appointment
Make an appointment via e-mail and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT VIA PHONE CALL
| international calls: | +386 4 275 13 25 |
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT BY POST
Write a mail to
Implantološki center d.o.o.
Mlaška cesta 109
4000 Kranj
Slovenia
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT IN PERSON
Make an appointment in person at the reception desk.
WORKING TIME
| Monday through Thursday | 8am - 7pm |
| Friday | 8am - 1pm |
| Saturday | closed |
| Sunday | closed |
WE ACCEPT PATIENTS WITHOUT PRIOR APPOINTMENT ONLY IN CASE OF EMERGENCY.
Toxins and bacteria can spread throughout the body from the oral cavity or tooth via blood and lymph. In this way, the infection can spread to other organs in the body.

